Dr. Chris Stanley
Scientific & Biomarker Advisor
Scientific & Biomarker Advisor

Scientific Consultant
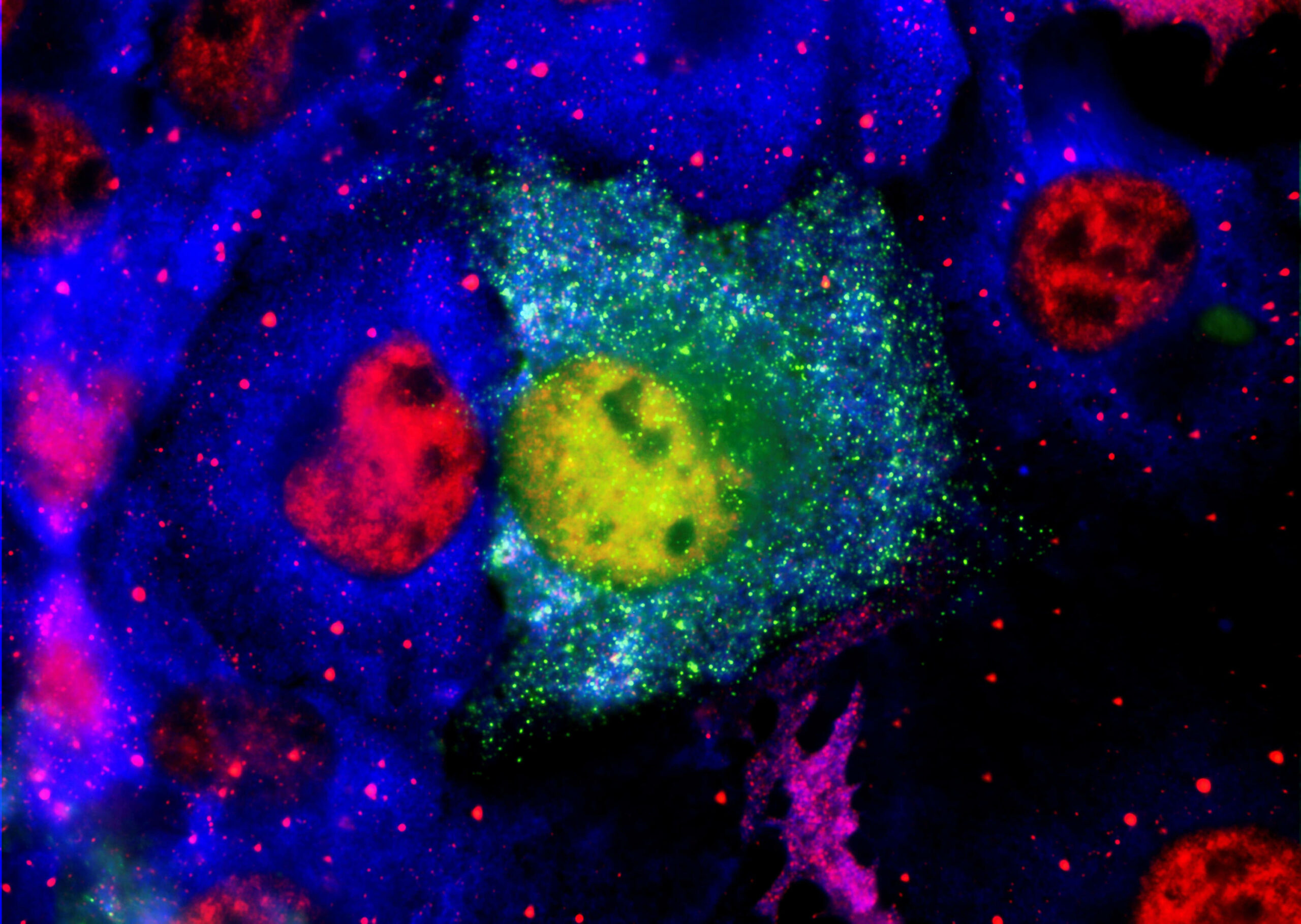
Dr. Stanley is the inventor/co-inventor of >40 published patents in the fields of in vitro diagnostics, medical devices and drug discovery. He has developed assays to detect and quantity brain-derived oligomeric and aggregated protein biomarkers in the blood including amyloid-ß and α-synuclein.
His current focus is on the diagnosis (and misdiagnosis) of Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease and other Lewy Body disorders, such as Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB) and Multiple System Atrophy (MSA). Dr. Stanley is networked with a number of partners including the Universities of Liverpool, Lancaster and Newcastle.
Dr. Stanley was a co-founder of CynapseDx and Circular1 Health.
CynapseDx Limited
Chris brought his expertise of measurement of oligomeric or aggregated proteins and purification of monoclonal antibodies from viscous cell cultures to CynapseDx. Previous investigations had measured oligomeric amyloid-ß in mouse and human brain extracts, but had been unsuccesful in blood. He succesfully applied the techniques developed to isolate stem cells from body fat, to isolation of oligomeric amyloid-ß and later
α-synuclein from blood from Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and Multiple Systems Atrophy patients.
He brings this expertise to PharmaKure’s development program.
CynapseDx patents
Chris is the inventor of the two CynapseDx patent applications acquired by PharmaKure in March 2021. The first describes means of measuring oligomeric proteins in blood samples. The second describes means to reduce the levels of toxic oligomeric proteins in blood as treatments for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
In addition to advising on implementation of the CynapseDx assays, he is responsible for maintaining the progression of two patent applications.
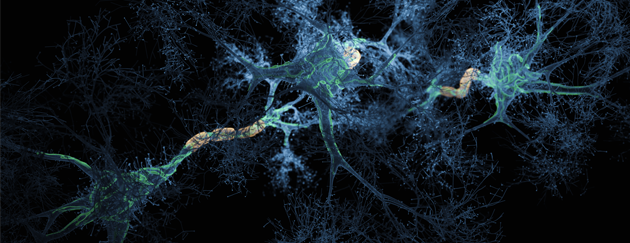
Oligomer measurment
Chris was an inventor on the technology for measuring oligomeric proteins which resulted in identification of the compounds in PK051 and the use of the technology to demonstrate disaggregation and prevention of aggregate formation of amyloid-ß